Permissions & Shell programming:
File and directory permissions:
chmod (Change mode): It is used to change the access permissions of files and directories.
Some different chmod permission notations are:
chmod +x test.sh: Gives permission to run the script.
chmod 444 test.sh: Changes file to read-only
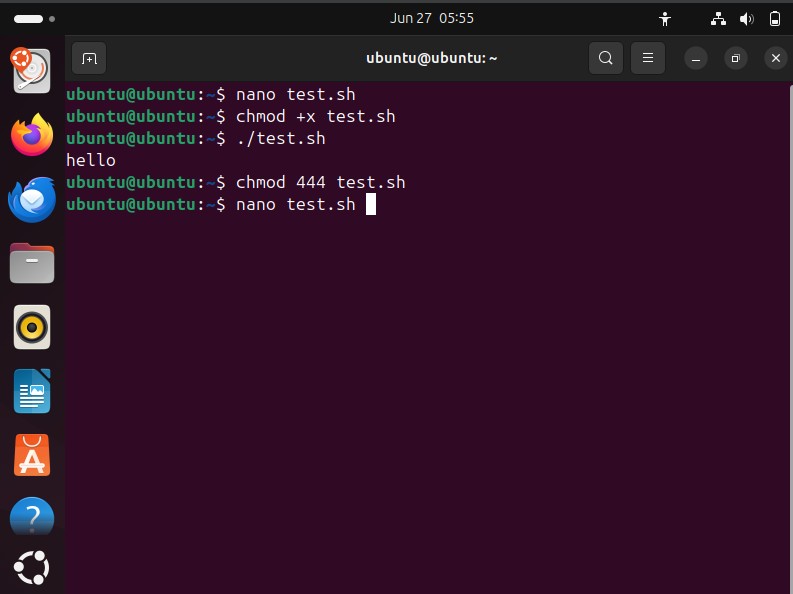
Result
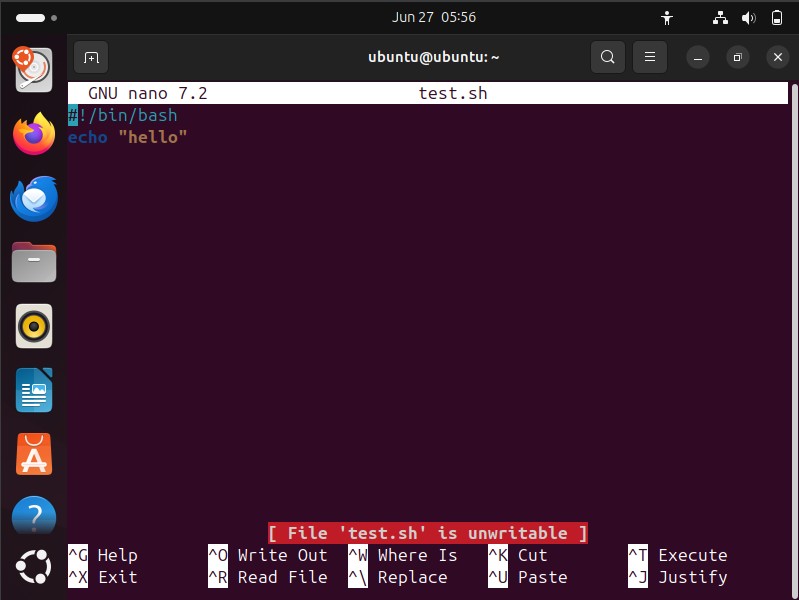
chmod 644 test.sh: Changes file such that only owner can edit it. For others it remain read-only.

Result

Redirection:
It allows user to redirect input and output functionalities to the files or folders.
Types of Redirection:
-
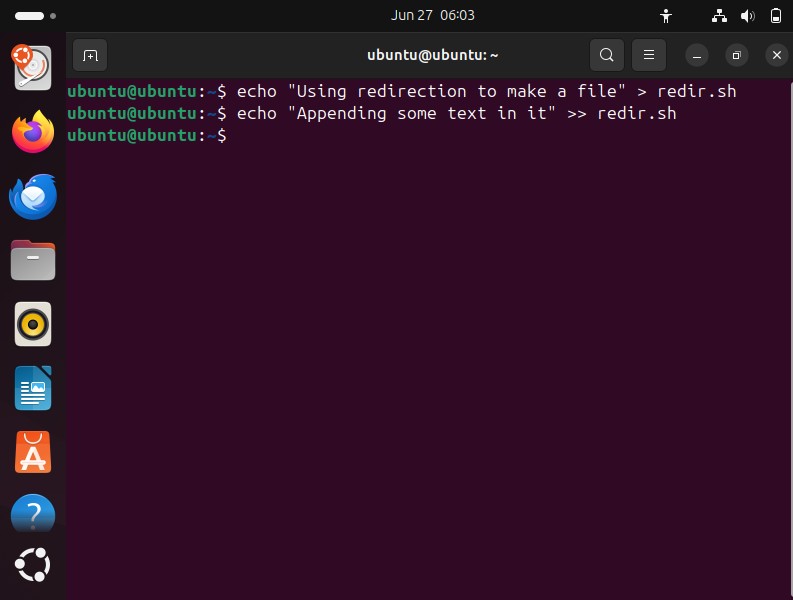
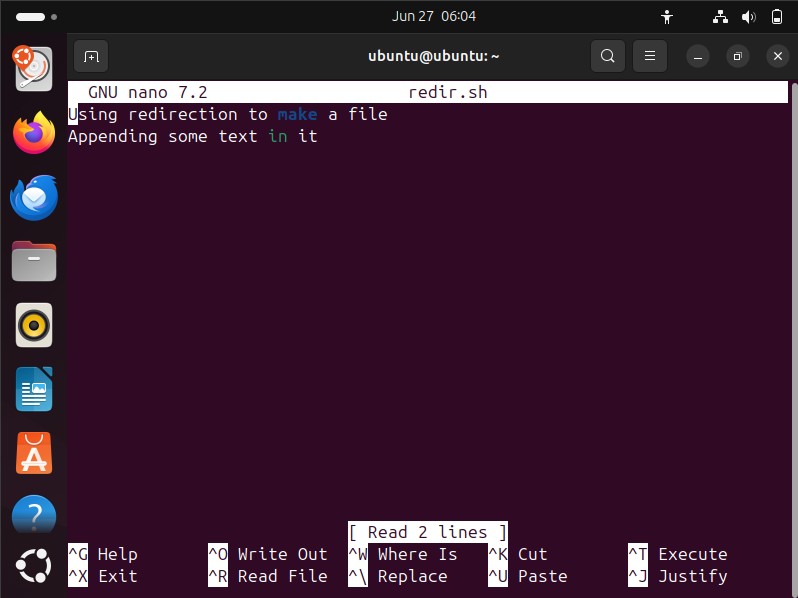
Overwrite Redirection (For stdout):
Redirects the standard output of a command to a file. If the file exists already contain script, it will be overwritten.
“>” standard output -
Append Redirection (For stdout): Append the output to the file without compromising the existing data of the file.
- Overwrite Redirection (For stdin):
Redirects the standard input of a command to a file.
“<” standard input
sorting with help of Redirection:

Pipe ‘|’:
The pipe is used to combine two or more commands, and in this, the output of one command acts as input to another command.
Pipe can be used for filteration.
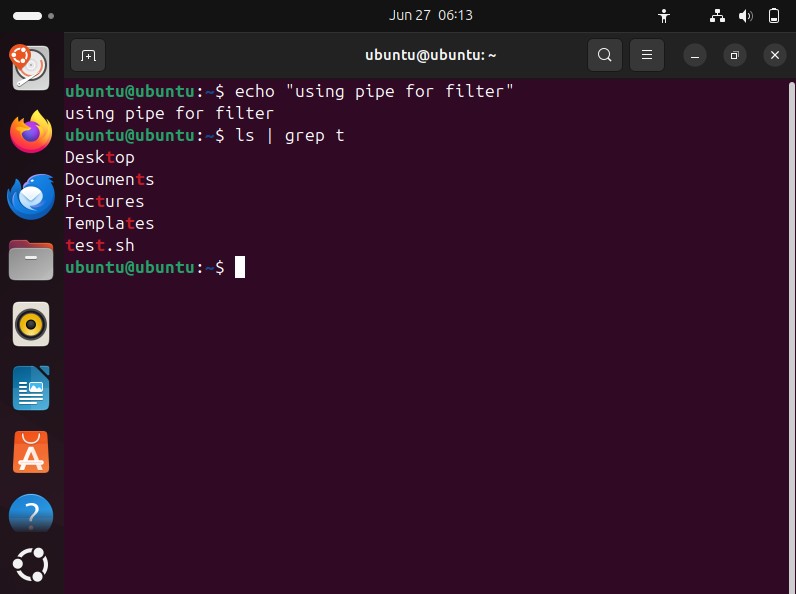
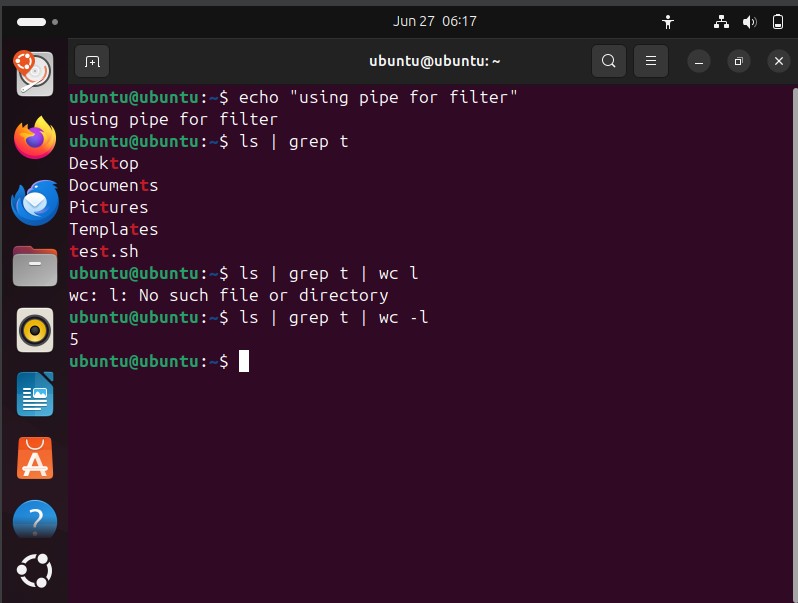
Multiple pipes can be used such as:
to find number of file/directory with ‘t’
File compression:
File compression reduces file size to save space or speed up transfer.
gzip:- Used to zip a file.
- Limitation: The original file is deleted.
gunzip:- Unzips the file.
- Flag
-k:- To zip the file
- Original file isn’t deleted.

Assignment:
Shell programming:
- Use of variables:

Output

- Comparing two variables:

Output

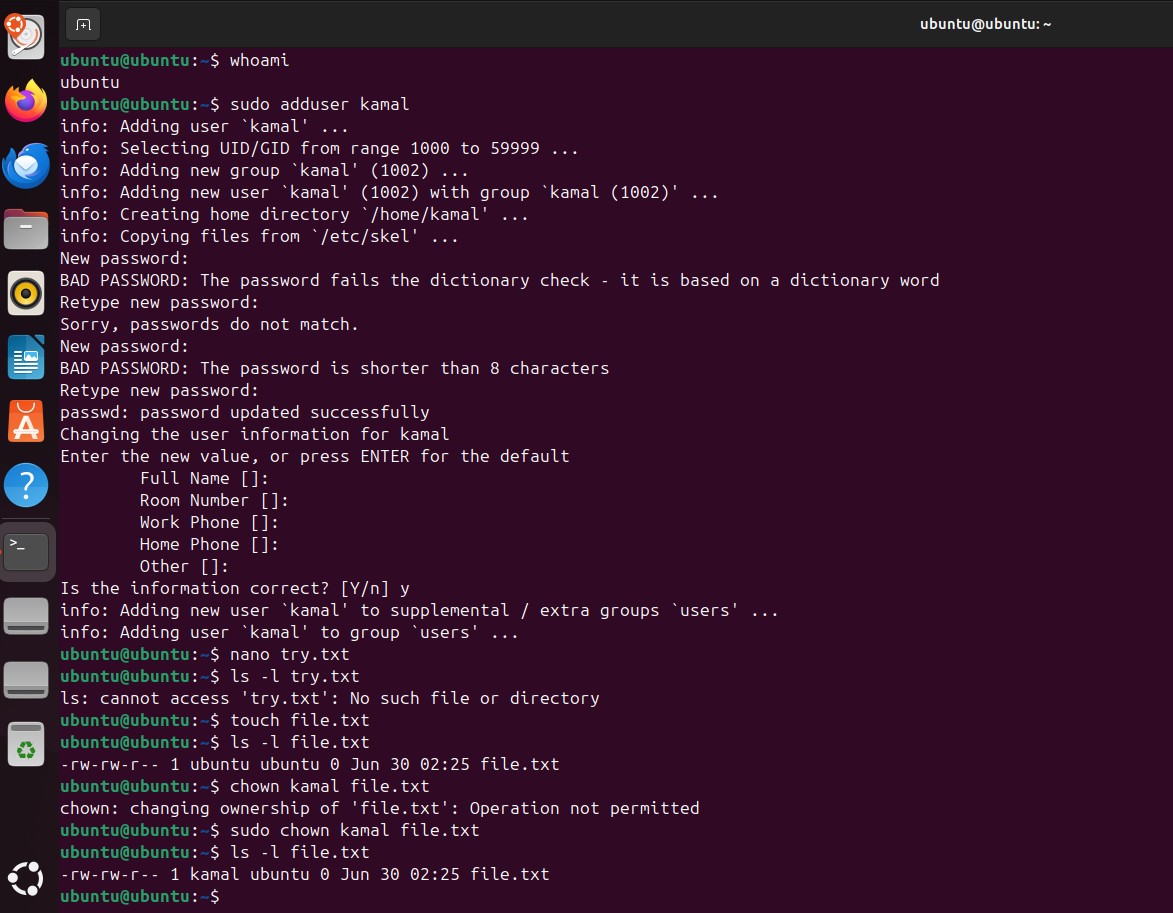
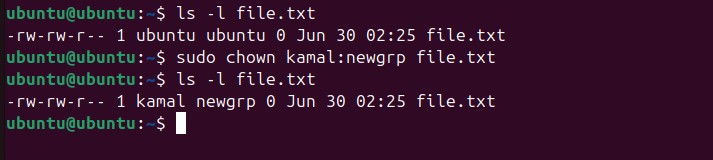
chown:
chown (short for change owner) is a command used to change the ownership of a file or directory.
How to Use chown:
- Check current ownership (optional).
- Run the
chowncommand. Usesudoif you’re not the current owner.
Changing owner only:
Changing group only:
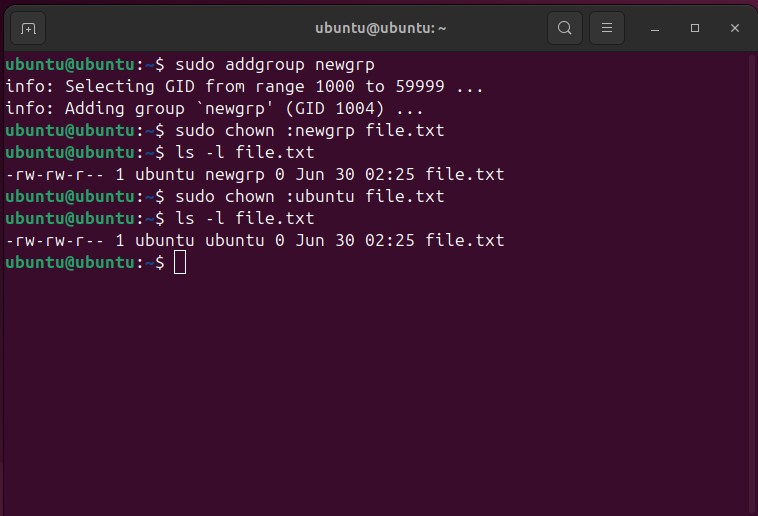
Changing both group and owner permissions:
Wild cards:
| Wildcard | Meaning |
|---|---|
* |
Matches zero or more characters |
? |
Matches exactly one character |
[abc] |
Matches one character from set |

Other short topics:
Partitioning Scheme:
A partitioning scheme is the way a hard disk or SSD is divided into sections (partitions) so the system can use it properly.
Its is used for:
- Separate system files from user files
- Install multiple OSes
- Create swap space
- Improve backup & security
Types of Partitioning Schemes:
1. MBR (Master Boot Record):
- Max 4 primary partitions.
- Supports up to 2 TB.
- Older, used with BIOS.
- less flexible
2. GPT (Guided Partition Table)
- Supports 128+ partitions.
- Works with disks >2 TB.
- Newer, used with UEFI.
- more flexible
Bare Metal Installation
- Installation directly using USB.
- Direct installation in computer hardware.
- No OS should be in between.