Day 6:
Safe mode:
Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode in Windows that starts the computer with a minimal set of drivers and services, which makes it easier to find and remove harmful malware and viruses without activating them.
Types of safe mode:
-
Safe Mode:
Used to diagnose and fix basic system issues. -
Safe Mode with Networking:
Includes network drivers and services. Allowing access to the internet or network drives for troubleshooting. -
Safe Mode with Command Prompt:
Loads a minimal environment with Command Prompt instead of the normal desktop interface
Recovery tools:
- The Recovery Drive utility in Windows is a tool designed to back up essential system files needed to restore a PC to its original state.
- It fixes problems that prevent Windows from booting.
- Rolls back system files and settings to an earlier point in time without affecting personal files.
OS repair:
It is used when the OS fails to boot or behaves abnormally.
Use repair commands:
- sfc /scannow – Scans and restores system files.
- DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth – Repairs corrupted Windows images.
- Bootable USB for repair and system reinstall.
Virus/Malware Symptoms:
- Slow performance
- Frequent crashes or freezes
- Slow startup
- Unexplained files or folders disappearing
- Unusual network activity:
- Malware can send or receive data, causing increased network activity, especially when your device is idle.
- Increased data usage:
- Malware can consume more data than usual, especially if it’s sending or receiving large amounts of information.
- Browser-Related Symptoms:
- Unwanted pop-up ads
- Browser redirects
Basic removal:
- Enter safe mode.
- Run Antivirus scan
- Delete suspicious Programs via Control Panel.
- Clear Temp files.
- Reset Web browser setting.
- Check startup Programs
- Update OS and antivirus.
Where to Keep Windows Backups?
Backups are essential for recovery in case of OS failure or data loss.
- External Drive: Recommended option for offline, safe backup storage.
- Separate Internal Drive (e.g., D:, E:): Better than storing on the system drive (C:), but vulnerable if the whole disk fails.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive, OneDrive, or Dropbox allow automatic syncing and access from anywhere.
Modern Internet Transmission (Wired Connections):
RJ45:
- RJ45 stands for Registered Jack 45.
- It is a standard connector used for Ethernet networking cables.
- RJ45 connectors are typically used to connect computers, routers, switches, and other networking devices.
- It has 8 pins (8P8C – 8 position, 8 contact) and connects twisted-pair cables like Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a.
- Commonly used for LAN (Local Area Network) connections.
Cat5, Cat6, Cat6e: Categories of twisted-pair cables used in wired networks, offering various speeds and shielding levels.
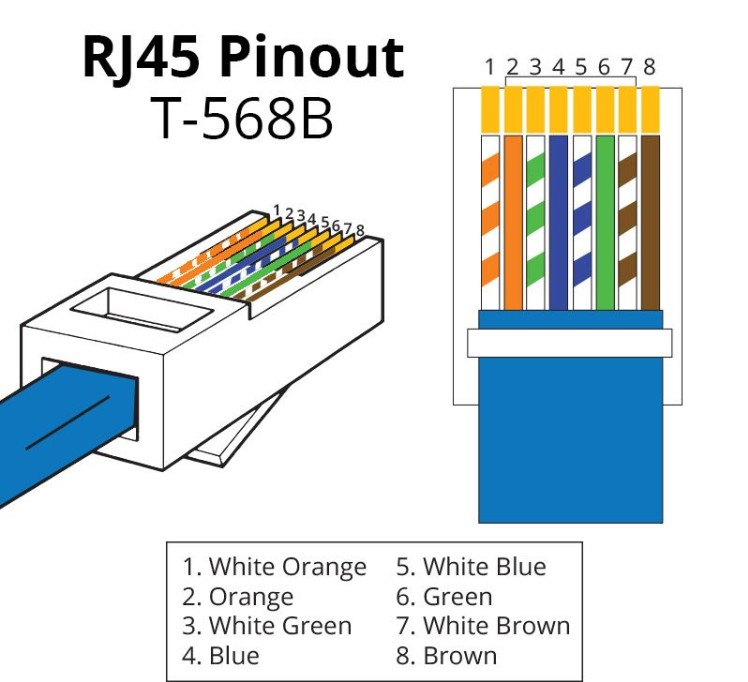
How to Make a RJ‐45 Cable:
- Strip the cable to remove 1 inch of the outer sheath.
- Untwist and straighten the wires inside of the cable
- Arrange the wires into the right order.
| Pin Number | Wire Color (T568B) | Signal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | White Orange | Transmit + (TX+) |
| 2 | Orange | Transmit – (TX–) |
| 3 | White Green | Receive + (RX+) |
| 4 | Blue | Unused / PoE + |
| 5 | White Blue | Unused / PoE + |
| 6 | Green | Receive – (RX–) |
| 7 | White Brown | Unused / PoE – |
| 8 | Brown | Unused / PoE – |
- Trim the wires into an even line 1⁄2 inch (13 mm) from sheathing
- Insert the wires into the RJ-45 connector.
- Stick the connector into the crimping part of the tool and squeeze twice.
- Remove the cable from the tool and check that all of the pins are down & test the cable.