Introduction to Git and Version Control:
What is Git and Why Use Version Control
- Git is a distributed version control system used to track changes in source code during software development.
- It helps manage code across multiple versions, developers, and updates.
-
Version control allows:
- Tracking changes over time
- Restoring previous versions of files
- Collaboration among multiple developers without conflicts
- Safe experimentation with new features
Git Architecture
1. Repository (Repo)
- A storage area where Git tracks all file changes
-
Can be:
- Local: on your computer
- Remote: on platforms like GitHub, GitLab
2. Working Tree
- The actual files and directories you’re currently working on in your system
- Reflects the current state of your code
- You make changes in the working tree before committing them
3. Index (Staging Area)
- A temporary area where you add files before committing to the repo
- It allows you to prepare exactly what will go into the next commit
- Acts as a buffer between the working directory and the repository

How to use Git? (With Command Line)
-
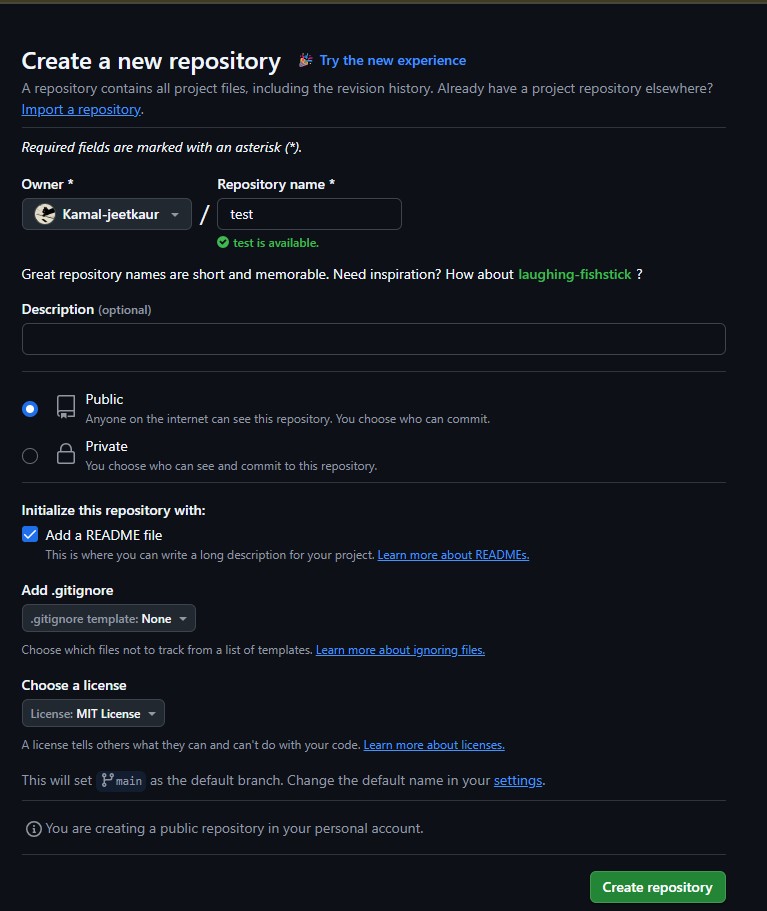
Create a repository
-
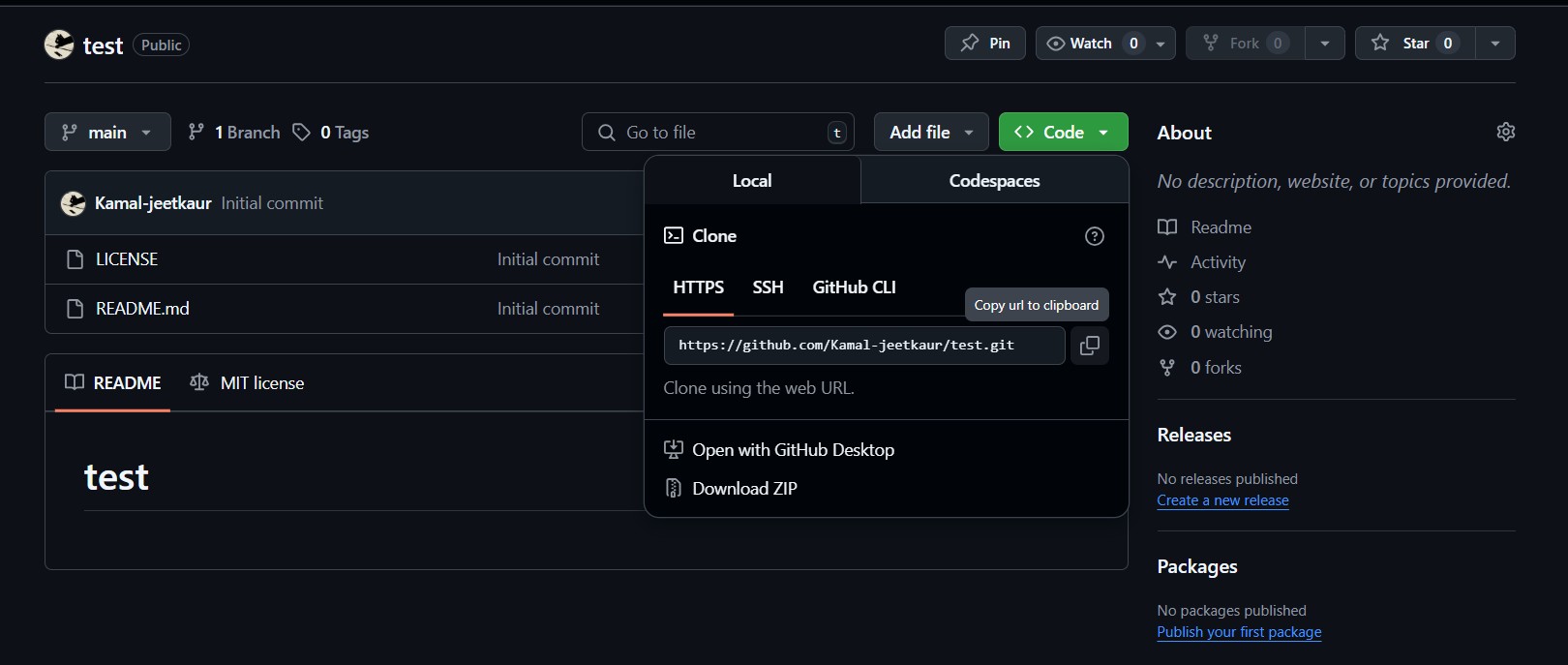
Copy the HTML line of the repo
-
Go to Git Bash
-
Run command:
git clone link -
Check if you got the repo cloned on your local dive by
ls -
Move inside the direcotry by
cd repo_name -
Check the content inside your repo (optional)
- Check status of the repo by
git status- If the response id ‘Up to date’, you are good to move forward
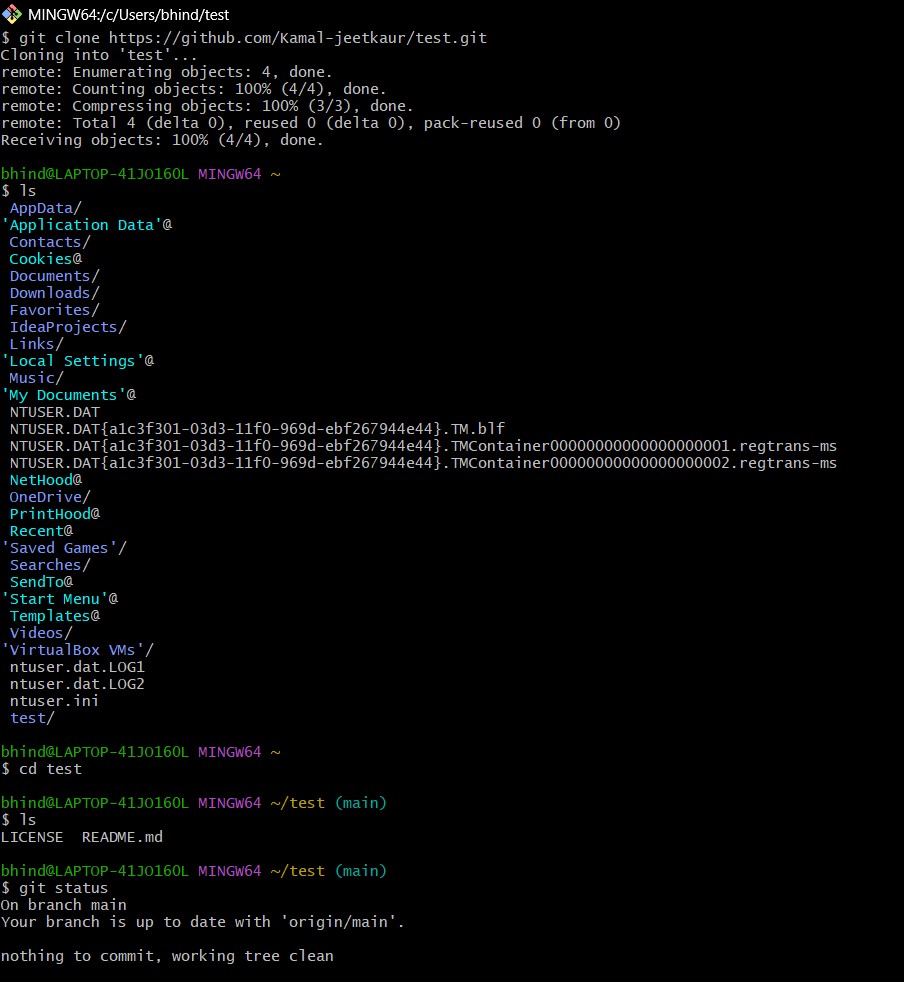
- If the response id ‘Up to date’, you are good to move forward
-
Create a new file by
touch file_name.html -
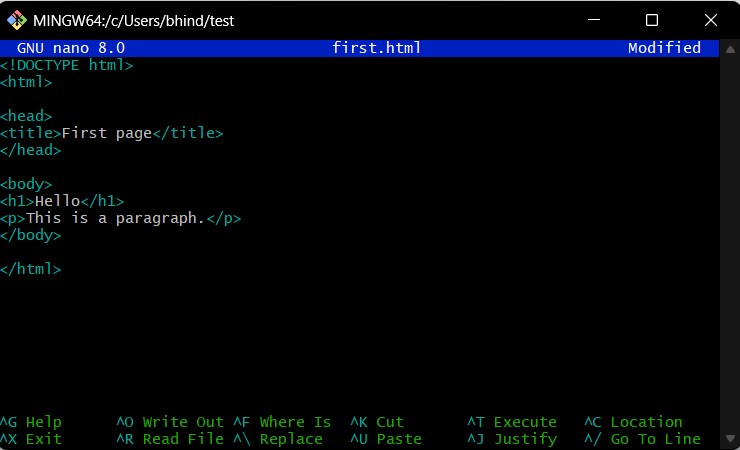
Open the file by
nano file_name.html, write your code and save it.
- Add by:
git add file_name.html
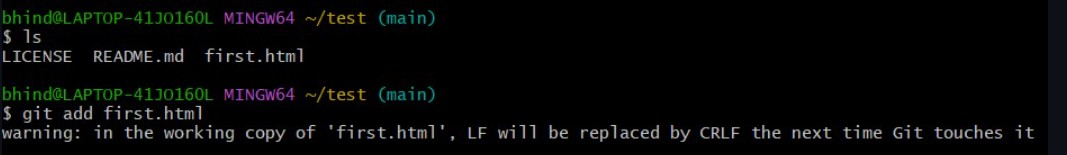
Warning Explained:
warning: in the working copy of 'first.html', LF will be replaced by CRLF the next time Git touches it
- Right now the file has Unix-style (
LF) endings, but since im on Windows, Git may convert it to Windows-style (CRLF) later.- It’s safe to ignore
git push origin main:- It directs and you get asked to authorize Git Credential Manager, which securely saves GitHub login credentials for pushing/pulling code.
- Click on ‘Authorize git-ecosystem’
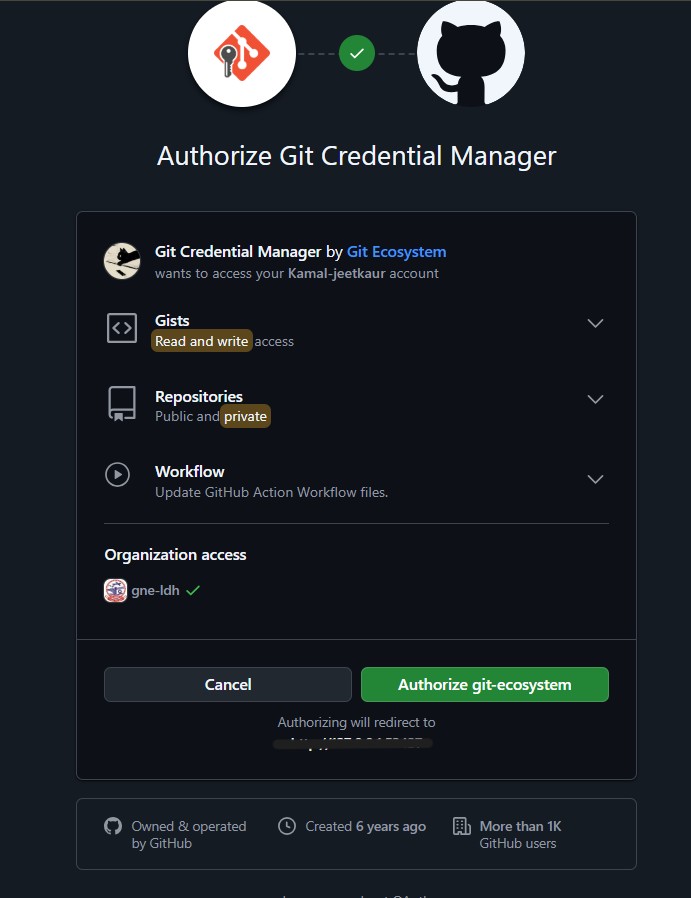
- Enter your password
- It directs and you get asked to authorize Git Credential Manager, which securely saves GitHub login credentials for pushing/pulling code.
- To commit:
git commit -m "message"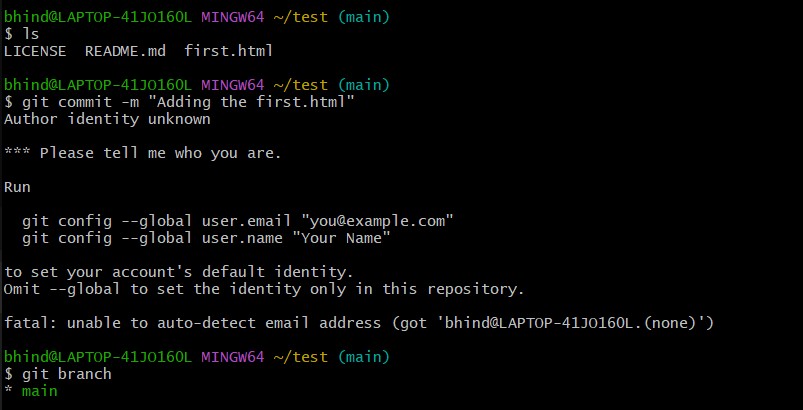
- I haven’t set a Git identity yet, so git commit cannot proceed.
- To fix this run:
- git config –global user.name “name”
- git config –global user.email “your-email@example.com”
email should match your Github email, but its not necessary for
name
-
Try
git commit -m "message"again, and push this by command:git push origin main: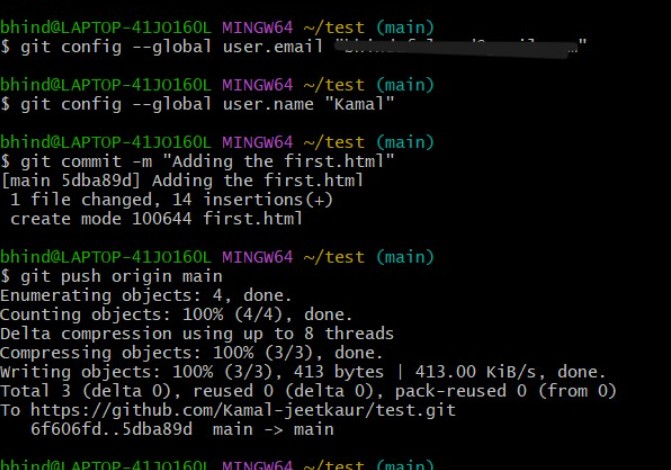
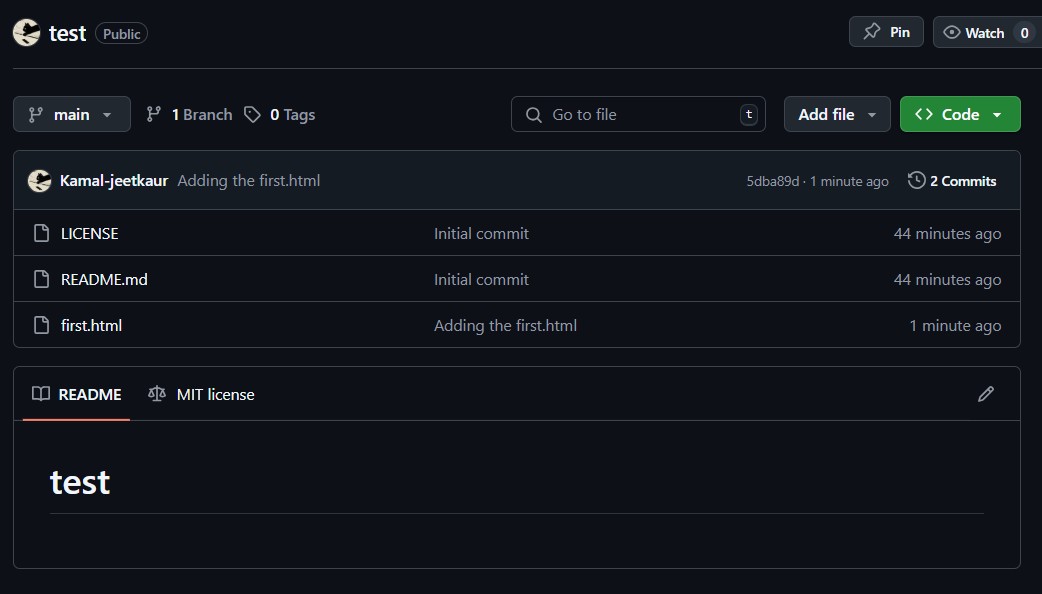
- Now you can see the file in your repo: